Using vSphere
vSphere is a software solution for deploying and managing virtual machines across a datacenter. With vSphere, datacenters can instantly provision servers, globally manage resources, and eliminate scheduled downtime for hardware maintenance.
Creating a datacenter
Create a datacenter as a container for hosts, virtual machines, resource pools, and clusters. Datacenters are always created under the root folder in the Hosts and Clusters inventory of a single vCenter Server, in a folder under the root folder, or under a vCenter object in a Linked Mode inventory.
To create a datacenter, select the vCenter Server system where you want to add the datacenter and select Actions > New Datacenter.
Creating a datacenter allows you to add hosts to it.
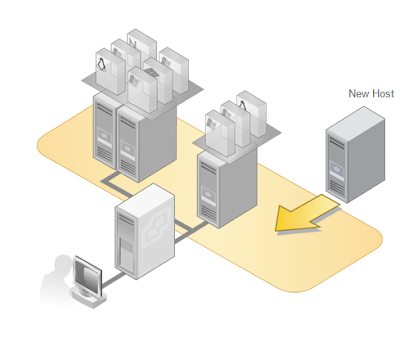
Adding a host
A host is a computer that uses virtualization software to run virtual machines.
To add a host to the datacenter, you must have a computer running ESX or ESXi software. When you add a host, it will be managed by the vCenter Server. After you add the host, use the vSphere Web Client to manage it and the virtual machines that run on it.
To add a host, select the datacenter you want to add the host to and select Actions > Add Host.
Creating a virtual machine
You can use several methods to create virtual machines to add to your inventory. You can create a new, blank virtual machine, import a virtual appliance, deploy from a template, or clone an existing virtual machine.
The vSphere Web Client provides a simple and flexible user interface from which you can create virtual machines. A wizard guides you through the steps to produce a complete and working virtual machine.
When you create a virtual machine, it’s created on the host you select. The virtual machine runs on that host and uses that host’s resources. You can move virtual machines from one host to another within the same datacenter.
1.Creating a new virtual machine
Creating a new virtual machine allows you to customize options such as number of processors, memory, network connections, and storage. You can create new virtual machines on hosts or clusters.
Before you create a virtual machine, decide which host or cluster the new virtual machine should reside on, the type of guest operating system you will install on the new virtual machine, and the location of the CD or image files for the installation. You also need appropriate vCenter Server permissions to create virtual machines.
To create a new virtual machine, select the host or cluster in the inventory you want to run the new virtual machine on and selectActions > New Virtual Machine.
A new virtual machine is like a physical computer with a blank hard disk. After you create the new virtual machine, you need to install a guest operating system on it. You can also change the settings of the virtual machine at any time.
Cloning a virtual machine
A clone is an exact copy of a virtual machine. When you create a clone, vCenter Server lets you customize the guest operating system of that virtual machine. You can run the new clone on any host within the same datacenter as the original virtual machine.
To clone a virtual machine, select the virtual machine and selectActions > All vCenter Actions > Clone. The Clone Virtual Machine wizard guides you through the steps needed to clone the virtual machine. You can clone a virtual machine in any power state.
During this process you need to:
- Give the virtual machine a name that is unique to other virtual machines and templates within the datacenter.
- Choose the host or cluster on which the new virtual machine will run.
- Assign a datastore for the virtual machine files.
During the Clone Virtual Machine Wizard, you can customize the guest operating system of the new virtual machine. Choosing this option launches the Guest Operating System Customization wizard.
Importing a virtual appliance
A virtual appliance is a prebuilt virtual machine that has an operating system and other software already installed. After a virtual appliance is imported, you have a fully functional virtual machine.
You can obtain virtual appliances from a variety of sources. VMware Virtual Appliance Marketplace has a large catalog of virtual appliances available for download. VMware or other vendors might also distribute virtual machines on CD or DVD disks.
You can install virtual appliances from a local hard disk if you have already obtained a virtual appliance, or you can enter the URL of a location on the Internet where a virtual appliance resides.
To start the wizard, select a host or cluster and select Actions > Deploy OVF Template.
Deploying from a template
When you deploy a virtual machine from a template, vCenter Server lets you customize the guest operating system of that virtual machine. You can run the new virtual machine on any host within the same datacenter as the template.
The Deploy Template wizard guides you through the steps for deploying a template. To start the wizard, select a template and select Actions > Deploy VM from this Template.
During this process you need to:
- Give the virtual machine a name that is unique to other virtual machines and templates within the datacenter.
- Choose the host or cluster on which the new virtual machine will run.
- Assign a datastore for the virtual machine files.
During the Deploy Template Wizard, you can customize the guest operating system of the new virtual machine. Choosing this option launches the Guest Operating System Customization wizard.
Creating templates
You can create a template with the following methods:
- Convert a virtual machine into a template
- Clone a virtual machine into a template
- Clone an existing template
When you clone a virtual machine into a template, a new template is created with the same configuration as the virtual machine, and the original virtual machine remains available in the inventory. Likewise, when you clone a template, a copy of the template is created and the original template remains.
To create a template, select a virtual machine from the inventory and select Actions > All vCenter Actions > Template > Convert to Template or Actions > All vCenter Actions > Template > Clone to Template. To clone an existing template, select the template and select Actions > Clone.
After you create a template, the vCenter Server adds the template in the Virtual Machines & Templates inventory tree or the VM Templates inventory list.
Migrating a virtual machine
You can move virtual machines by using migration — the process of moving a virtual machine from one host to another. Migration options include the following:
vSphere vMotion (Live migration)
vSphere vMotion moves a running virtual machine from one host to another. If the virtual machine is powered on and uses storage and network options available to the new host, it can be moved without stopping applications or disrupting the guest operating system.
vSphere vMotion moves a running virtual machine from one host to another. If the virtual machine is powered on and uses storage and network options available to the new host, it can be moved without stopping applications or disrupting the guest operating system.
Cold migration
Cold migration moves a powered off virtual machine from one host to another. Migration can be performed by dragging the virtual machine from one host to another within the same datacenter.
Cold migration moves a powered off virtual machine from one host to another. Migration can be performed by dragging the virtual machine from one host to another within the same datacenter.
You can move virtual machines between hosts within the same datacenter, but you cannot move virtual machines across datacenters. You can move virtual machines manually, or you can set up a scheduled task to perform the migration.
Using folders
You can group the following inventory objects in folders to further refine object grouping within your inventory: Datacenters, virtual machines and templates, hosts and clusters, datastores and datastore clusters, and network objects.
The objects grouped within a folder must be of the same type.
To create a folder:
- Select a vCenter Server system and select Actions > New Folder.
- Select a datacenter and select Actions > All vCenter Actions > New Host and Cluster Folder or New Network Folder orNew Storage Folder or New VM and Template Folder.
To add an object ot a folder, select the object and select Actions > Move To. Select the folder as the destination for the object.
To delete a folder, select the folder in the inventory and selectActions > All vCenter Actions > Remove from Inventory. If you delete a folder, you delete all of the inventory items within it. If the items in the folder are hosts, they are disconnected from the vCenter Server system.
Creating clusters
When you create a cluster, decide whether to enable the vSphere HA or vSphere DRS solutions on it. You can enable either of these options by using the wizard during cluster creation.
To create a cluster, select the datacenter to add the cluster to. Then select Actions > New Cluster.
Add hosts already in the inventory to the cluster by selecting the cluster and selecting Actions > Move Hosts into Cluster. Then select the hosts to add. You can add new hosts directly into the cluster by selecting the cluster and selecting Actions > Add Host
Creating resource pools
When you create a resource pool, you can specify resources, such as CPU and memory shares, for a set of virtual machines. You can specify reservations, limits, and shares that determine how the resources are allocated.
To create a resource pool, select a host and select Actions > All vCenter Actions > New Resource Pool, or select a cluster and select Actions > New Resource Pool. The New Resource Pool wizard guides you through the creation process.
After you create a resource pool, you can add virtual machines to it by dragging them onto the resource pool object. Virtual machines added to a resource pool share the CPU and memory resources according to the resource pool’s configuration.









